
Hair Loss Frequently Asked Questions
Why Is My Hair Thinning?
Healthy individuals can lose about 100 hairs a day. Though this may sound like a lot, it’s not usually enough to cause a noticeable thinning of the scalp hair, since new hair is growing in at the same time. For hair loss to occur, there must be a disruption of the cycle of hair growth or the hair follicle must have been destroyed and replaced with scar tissue.
Hair loss is commonly caused by one or more of the following factors:
- Heredity: Most hair loss is hereditary, which is known as male-pattern or female-pattern baldness. This typically occurs gradually with the aging process and follows a predictable pattern. For men, this pattern is a receding hairline and bald spots, whereas women tend to get overall thinning hair.
- Hormonal changes and medical conditions: In both men and women, many conditions can result in permanent or temporary hair loss. These can include thyroid issues, alopecia, scalp infections, trichotillomania or hormonal changes related to aging or pregnancy.
- Medications: Hair loss can be a side effect of drugs used to treat arthritis, cancer, heart conditions, depression, high blood pressure, gout and other health conditions.
- Radiation: Radiation therapy near the scalp may cause hair loss or a change in the growth patterns.
- Stress: Following extremely stressful situations, many people experience a temporary thinning of the hair that recovers in time.
- Hairstyles and hair treatments: Tight hairstyles can cause traction alopecia, which is a specific type of hair loss that occurs in the areas where hair is often pulled. Hot oil treatments, excessive chemical styling and other processing can also cause inflammation of the hair follicles that leads to hair loss.
What Is Male-Pattern Baldness?
Male-pattern baldness is a hereditary balding pattern that usually starts in the twenties with receding hair at the temporal peaks or thinning at the crown. Over time, this can progress from the top of the head to the crown, which leaves a ring of hair around the sides and back of the scalp.
Can Hair Loss Be Caused by Hats or Hair Products?
Though it’s a common belief that hats and helmets cause hair loss, that myth has been long debunked. There’s no evidence that wearing a hat or a helmet can cause or contribute to hair loss.

As far as hair products, it’s generally rare, but some products have been known to cause hair loss. This isn’t specific to shampoo, conditioner, hairspray or any general product, but more the result of use of a specific brand that has had claims of hair loss from customers.
There’s also no evidence that washing your hair too often can cause hair loss, though rough washing, brushing and combing, as well as wearing certain hairstyles can contribute to hair loss. These include tight braids, ponytails, cornrows and other hairstyles that pull the hair tight, which damages the follicle over time.
What Are the Symptoms of Hair Loss?
Hair loss appears in different ways on different individuals, depending on the underlying cause. It may appear gradually, or it may start with large chunks of hair missing, and it could be temporary or permanent.

The symptoms of hair loss include:
- Gradual thinning on the top of the head: This is most common in both men and women, though men are more likely to experience a receding hairline in an M pattern. Women are more likely to have a widening part in their hair.
- Patchy bald spots: Some individuals experience hair loss in smooth, circular bald spots on the scalp, beard or eyebrows. This may also be accompanied by pain or itchiness.
- Loose hair: Extreme stress can cause the hair to loosen at the root, which may cause handfuls of hair to come out during washing, combing or brushing. This type of hair loss is usually over the entire scalp, not individual bald spots.
- Full-body hair loss: In individuals undergoing chemotherapy, there may be a total loss of all body hair. This usually resolves once the treatments stop.
- Scaly patches: With ringworm, individuals will experience scaly patches all over the scalp, as well as redness, broken hair, swelling or oozing.
What Are the Risk Factors for Hair Loss?

Many factors can impact hair loss, such as:
- A family history of balding on either the paternal or maternal side, though male-pattern baldness is more likely to come from the males on the maternal side.
- Age.
- Extreme weight loss.
- Medical conditions, such as lupus.
- Extreme stress.
How Can I Prevent Hair Loss?
Though genetics are the predominant factor in hair loss, there are many types of hair loss that can be avoided.

Here are some tips to prevent hair loss:
- Avoid tight hairstyles.
- Avoid twisting or pulling your hair.
- Be gentle while washing and brushing your hair.
- Avoid heat processing and chemical processing.
- Avoid medications that are known to cause hair loss.
- If you smoke, quit.
- Protect your hair from ultraviolet light.
Though these methods won’t prevent all hair loss, they can help prevent or slow certain types of hair loss.
What Can Cause Rapid Hair Loss?
While a small amount of hair loss or thinning hair is normal, and may even be temporary, a sudden loss of excessive amounts of hair may indicate a serious health problem.
With sudden, rapid hair loss, there may be an underlying internal or systemic disease or condition. Alopecia areata, for example, occurs when the body’s immune system attacks the hair follicles. Lupus and diabetes can also cause sudden hair loss, due to changes in the immune system or hormonal fluctuations.
If you’re experiencing sudden hair loss, it’s important to consult a physician to identify and treat the underlying condition and prevent further hair loss.
What’s the Difference Between Alopecia Areata, Alopecia Universalis and Alopecia Totalis?
All of these types of alopecia are autoimmune disorders, which means that the body’s own immune system is mistakenly attacking the hair follicles, triggering hair loss. The main difference between them is the pattern and extent of hair loss.
With alopecia areata, there are smooth, circular patches of hair loss. With alopecia totalis, there’s total hair loss on the scalp. With alopecia universalis, there’s hair loss all over the body, including the eyebrows and eyelashes.
What Helps Thinning Hair?
The first step in treating thinning hair is addressing the underlying condition. For many people, the cause of thinning hair is temporary and treatable, such as extreme stress levels or hormone imbalances. If you’re experiencing thinning hair, your physician will be able to help you rule out serious medical conditions, hormone imbalances or nutrient deficiencies so that you can address the cause of your hair loss.
If the hair loss is permanent, treatment options like Rogaine are something to consider. Rogaine, the only FDA-approved over-the-counter treatment for hair loss, is applied topically to the scalp to encourage hair growth. Propecia, a prescription hair loss medication for men, is also an option.
Regardless of whether your hair loss is permanent or temporary, it’s best to eliminate possible causes to slow or prevent future loss. Eating a healthy, balanced diet, minimizing stress and avoiding tight hairstyles and heavy processing will preserve the hair that’s left.
How Can I Regrow My Hair?
Regrowing lost hair depends on the underlying cause. With androgenic hair loss, or hereditary hair loss, the focus is primarily on halting the current hair loss to preserve what’s there.
With factors that cause temporary hair loss, such as poor diet, lifestyle choices, stress, traction alopecia or medications, hair loss can be reversed by correcting the underlying condition. Over time, you will notice that the hair you’ve lost will grow back with proper care and maintenance.
There are also remedies and topical treatments that may help your hair grow back, such as multivitamins designed for hair growth and minoxidil, which is better known as Rogaine. While these treatments have promise, the results vary.
The most promising option for men and women with permanent hair loss is hair restoration. This procedure uses full, healthy hair from other areas of the body that match the hair on your scalp, which is then transplanted using “micrografts.” Each of these individual hair follicles are surgically implanted into the scalp and grow normally to provide a natural, full head of hair.
How Is Hair Loss in Females Treated?
Though female-pattern baldness doesn’t get much attention, it affects a significant portion of the population and comes with devastating psychological effects. Fortunately, hair loss in women could be caused by a variety of short-term factors, such as pregnancy, menopause, stress, medications and other factors, so the hair will grow back when the event has passed.

If the hair thinning is a result of a medical condition, such as hormone imbalance or a thyroid disorder, treating the underlying cause is the first step toward halting further hair loss and giving the hair a chance to grow back.
If the hair thinning is a permanent type, there are still options. Rogaine for women is a possible treatment, as well as spironolactone, which is a drug that’s used to treat high blood pressure and heart conditions. Off-label, spironolactone is used to regulate hormones and treat acne and hair loss.
In more extreme cases, or if the condition doesn’t respond to less invasive treatments, follicular unit extraction (FUE), or hair transplantation, is a viable option.
How Do Hair Transplants Work?
Hair transplants have been around since the 1950s, but the techniques and technology have changed significantly over the years. Now, there are two types of transplant surgeries: follicular unit strip surgery (FUSS) or follicular unit extraction (FUE).
With FUSS, the surgeon takes strips of skin from the scalp, which is then divided into thousands of tiny micrografts, each with an individual hair follicle. The number and type of grafts you need depend on your hair type, color, quality and the area that requires a transplant.
With the FUE procedure, the back of your scalp is shaved, and the follicles are removed individually. The sites of harvest are hidden by surrounding hair as it regrows its length..
Beyond that, both procedures are similar. After the grafts are prepared, the recipient area is cleaned and numbed. Small incisions are created with a scalpel or needle, and the grafts are transplanted into each of these sites.
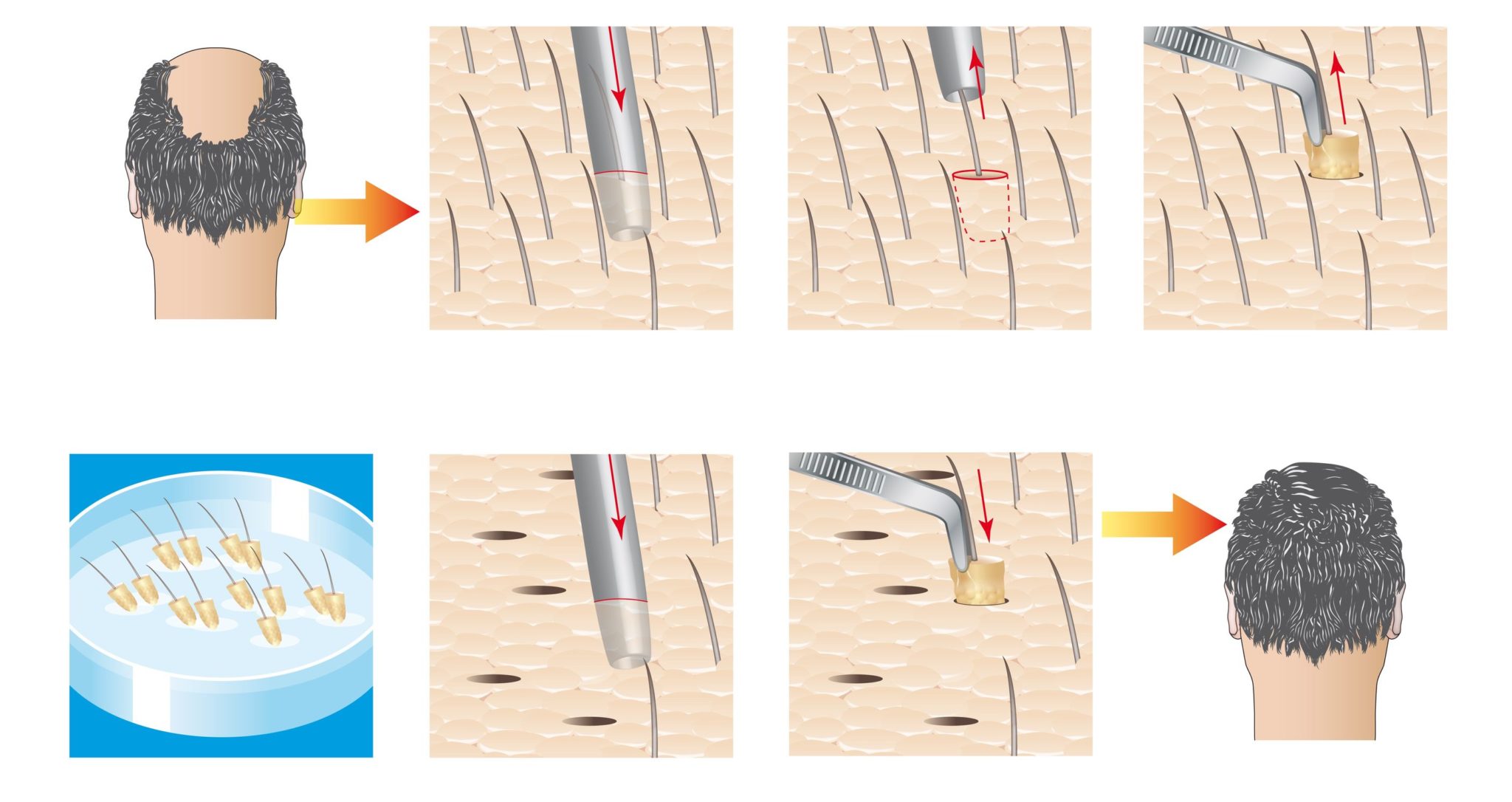
The process can take several hours, depending on the size of the transplant area. If you still experience hair loss in the future, the procedure may be repeated as long as the donor site is still thick enough..
Following surgery, you can expect your scalp to be tender and you may be prescribed pain medication, antibiotics or anti-inflammatory drugs. You will also wear bandages over your scalp for a few days, but you can usually return to work within a week of the procedure.
After two or three weeks, the stubble of transplanted hair will fall out, but the transplanted follicles are still alive. New hair growth will typically appear about four to five months post procedure. Most people experience the greatest hair growth after six to nine months.
Does Hair Transplant Surgery Result in Permanent Hair Growth?
Hair removed from the donor area of the scalp is genetically programmed to continue growing over the course of your life, without being impacted by male pattern baldness. As a result, transplanted hair will continue to grow.
Will Hair Transplants Bring Back Normal Hair Thickness?
Based on what can be borrowed from the donor region, it is not always possible to restore hair to its original thickness. However, individuals with thick hair outside of the pattern of baldness may be able to achieve noticeably thick, full hair after transplant. Density and coverage vary from person to person.
Will My Hair Transplant Look Obvious?
Natural-looking hair transplants are an art. Many surgeons who are unskilled or are using outdated techniques may cause unnatural implants, or the “plugs” of the past. Because of this, it’s important to choose a clinic with skilled professionals who have experience with hair transplant surgery.

Though it’s routine, hair transplant surgery still carries risks, both in health and the psychological impact of the results, so it’s important to be sure you’re choosing a reputable clinic with experienced staff members.
Is a Hair Transplant Painful?
Hair transplant surgery uses a local anesthetic to eliminate the discomfort during the surgery itself. Following surgery, you may feel minor discomfort during the healing phase, but you’ll be prescribed pain medication to keep you comfortable. For most patients, the pain subsides within a few days.
What Are the Risks of Hair Transplant Surgery?
There are risks to any surgery, such as infection, scarring or bleeding. The risks with hair transplant surgery are rare, however, especially when performed by a skilled surgeon.
The other risks to hair transplant surgery involve the final look and expectations of hair restoration. Because of this, it’s important to thoroughly research your hair transplant surgeon, ask questions during the consultation and be sure you and your surgeon are on the same page as far as your goals and expected results. The best hair restoration is one where no one can tell you have had a hair restoration.
Is It Better to Have Hair Transplant Surgery As Soon As Hair Loss Begins?
Deciding to undergo hair transplant surgery is an individual decision that takes many factors into account. However, the best time to begin preventative treatment would be at the onset of symptoms.

Unfortunately, baldness is progressive and unpredictable, so it’s difficult to determine when the best time is for transplant surgery without a thorough evaluation. With young patients, a concern is running out of donor hair and limiting surgical options, as well as insecurity or immaturity that may impact goals and expectations. In this case, it’s up to the surgeon to consider all the options for a particular patient to be sure that it’s in their best interest and offer guidance about the decision.
Individuals experiencing hair loss may also have panicked feelings, believing that they need to stop hair loss and restore the lost hair immediately. This can lead to unrealistic expectations for what hair transplant surgery can do. Ideally, a hair transplant patient is making an informed decision and demonstrates the patience necessary to enjoy the benefits of hair restoration.
Visit Vegas Valley Hair Restoration
If you’re facing hair loss and considering hair transplant surgery, visit Vegas Valley Hair Restoration. We’re proud to be the only NeoGraft provider in Southern Nevada where services are provided by a board-certified surgeon, Dr. Simon.
We offer NeoGraft Hair Restoration, a minimally invasive, FDA-approved hair treatment with no incisions, sutures or scars, and hair transplant and restoration surgery to restore your own living and growing hair. Regardless of your level of hair loss or the area affected, we can provide you with natural-looking results that restore your confidence.
If you want to learn more about our hair restoration options and find out more about Dr. Simon, visit Vegas Valley Hair Restoration. Read more about our services, check out some before and after photos and contact us to schedule your consultation today!